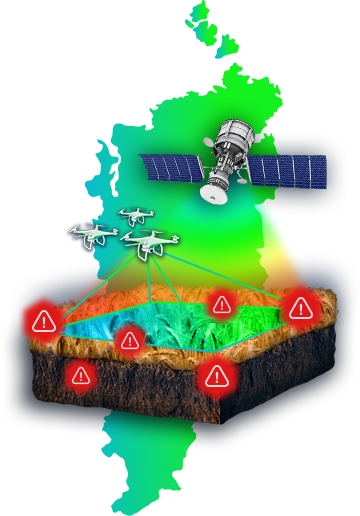
Digital solutions for monitoring fertility and assessing fertilizer application on your plot based on artificial intelligence


Avoid overfertilization and reduce air and water pollution

Improve cost efficiency of your farming

Get all the important details

Perfect for small and medium sized farms

One of the most sophisticated analytical model on the market

Amazing tool for precision agriculture
Get 12 months of data in real time
The AI model was developed by agricultural scientists
Vavilov-Index is an innovative web application for smart agriculture. Our product allows for soil fertility assessment and monitoring fertilizer application on agricultural lands based on artificial intelligence.
The developed architecture of artificial intelligence with one-dimensional convolutional layers and a recurrent LSTM layer enables the processing of large datasets coming from various sources, such as multispectral multi-temporal Earth remote sensing data, geoinformation library data starting from 1992, statistical data on NDVI, GNDVI, EVI, CVI indices, soil research data, and biological productivity of cultivated crops.
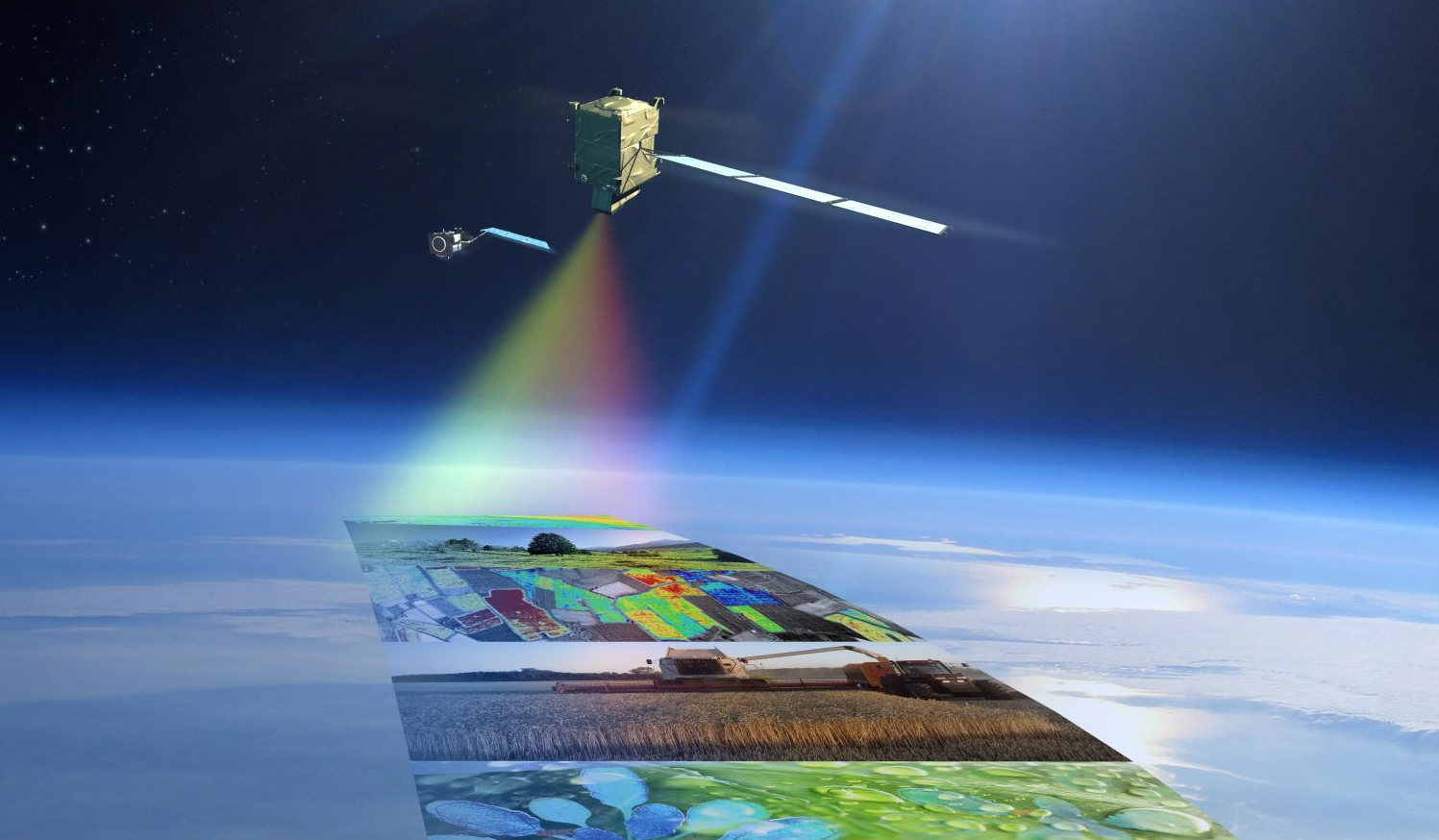
Vavilov-Index allows for the accurate assessment of nutrient presence in the soil with up to 97% accuracy and calculates the minimum fertilizer application rate.
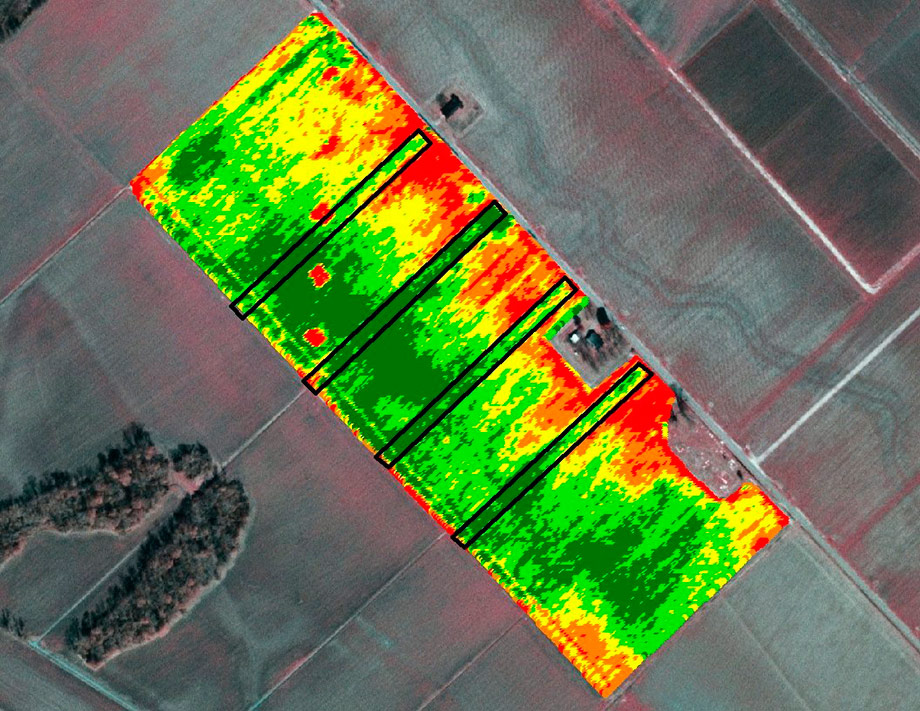

Our solution will assist agricultural producers and farmers in obtaining Variable Rate Application (VRA) digital fertilizer application maps without the need for special equipment and sample collection. This significantly streamlines the crop management process, reducing both time and costs.

Fertilizer application is a crucial component of sustainable agriculture, aimed at maintaining soil fertility and replenishing nutrient deficiencies caused by plant extraction.
Over the past two years, the cost of fertilizers has increased by 46%, leading some producers to reduce fertilizer consumption from 300 kg/ha to 200 kg/ha. This has resulted in a significant decline in crop yield and the profitability of producers.
Various methods exist to address the issue of precise fertilizer application, including soil sample collection followed by laboratory analysis, satellite-based remote zoning, and drone-assisted video recording.
However, all currently available methods for the rational use of fertilizers have several drawbacks:
These limitations prevent small and medium-sized agricultural enterprises and farmers from adopting these technologies. Considering the rising cost of fertilizers, this leads to an increase in the cost of production and a reduction in consumer demand.